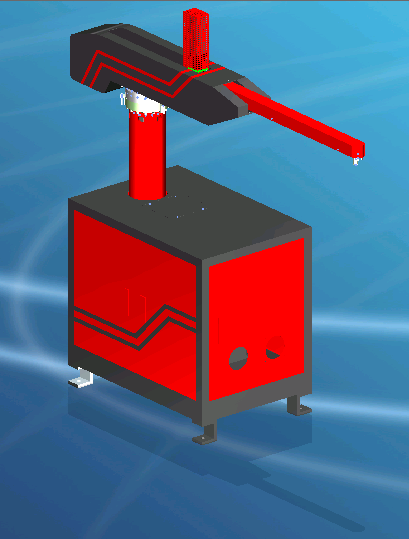
The robot is driven by pneumatic, hydraulic, electric and mechanical four. Stamping robots are mostly pneumatically or hydraulically driven.
According to the different forms of arm movement, the robot can be divided into four forms: Cartesian coordinate, cylindrical coordinate, polar and multi-joint.
Arm in the Cartesian coordinate system of the three coordinate axes for a straight line movement, that is, the arm before and after the telescopic, up and down movements and left and right movement. This form of coordinates occupies a large space and the scope of work is relatively small, inertia, it applies to the work position in a straight line.
Arm for the front and rear telescopic, up and down movements and in the horizontal plane of the action. Compared with the Cartesian coordinates, the occupied space is smaller and the working range is large, but because of the relationship between the structure of the structure, the height of the lowest position is limited, so can not crawl the object on the ground, inertia is relatively large. This is the use of a wider range of manipulators in the form of coordinates. , Arm for the front and rear telescopic, up and down the pitch and swing around the action. Its biggest feature is a simple body to get a larger range of work, and can grab objects on the ground. Its movement inertia is small, but the arm swing angle error caused by the arm will be enlarged, the arm is divided into two arms and the arm, the size of the arm connected by the elbow, and the arm and the column connected between the shoulder Joints, coupled with the wrist and the wrist between the wrist, multi-articular manipulator can complete almost as the action of the staff. Multi-articulation manipulator is flexible and has little inertia. Can grasp the workpiece close to the base, and can work around the obstacles. Multi-articulation manipulator wide adaptability, after the introduction of computer control, its action control can be completed by the program, but also through the memory simulation. Is the direction of development of the robot.